I’m sure you’ve had them your whole life, or you are just recently starting to see them. Those little black fuzzy things floating around your eye. These pesky critters are commonly known as floaters. Eye floaters are one of the common problems that affect people of age above 50. These floaters are tiny moving bits that appear in your eye. They can be prominent when you are looking at something of bright color. These floating objects may be annoying, but they usually do not disturb your vision. Sometimes particularly large floaters can disturb the vision. But this usually happens only under certain types of lighting. In most instance, people get used to living with floaters and be able to see without them being in the way, and these floaters become less noticeable in a few months or a few years. Only when floating objects become unbearably annoying can a treatment be considered.
Symptoms of eye floaters:
- Eye floaters, when visible, are usually rather minor. As a rule, they “run away” when you try to focus on them. Eye floaters can appear in various forms:
- Black color or gray color dots
- Twisted lines
- Threadlike translucent strands
- Ring form
Eye floaters, as a rule, do not disappear with time, although they can improve, i.e. become less noticeable, and hence, become less annoying.
Causes of eye floaters:
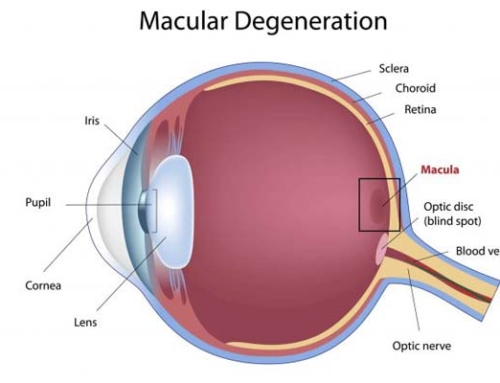
The back portion of the eye is covered with a jellylike substance called the vitreous body. With age, the proteins that make up the vitreous body shrinks and becomes small dots or pieces. The transparent vitreous gel, which completely fills the entire back compartment of the eye, does not decrease in size over time. These dots cause shadows especially, on the retina, and these small dots are floaters. However, when the vitreous removes from the retina, you may experience flashes. When you experience flashes, you should go and see your doctor immediately. All these events can occur at any time of your life, but most often they occur above 50 years of age.
- Major reasons for the development of eye floaters are
- Any form of eye injuries
- Retinopathy that results from the complication of uncontrolled diabetes
- Specialized form crystal shape deposits in the body of vitreous
- Rarely, eye tumors
Further, eye floaters can also be associated with severe eye disorders that require immediate attention from a doctor. The severe disorders are
- Retinal detachment or tear
- Bleeding inside the eye, especially in vitreous
- Fungal infections
- Viral infections that affect the vitreous body and the retina
- Autoimmune diseases that attack eye.
In addition, the unique form of eye floaters can be associated with a visual aura during headaches like migraines. Also, certain types of migraines can be associated with a flickering and kaleidoscopic type of visual images with some visible movement.
When to see a doctor:
If you have only a few floaters that do not change over time, then, as a rule, they do not indicate a serious problem. It is important to consult an eye doctor if:
- Deterioration of floaters over time, especially if the changes are abrupt at the very beginning
- You see flashes of light or lose sight when there are floating objects in the eyes
- You observe floaters after an eye surgery or eye injury
- You experience eye pain with floating objects in the eyes.
Treatment:
Usually, eye floaters do not need any treatment. If they become distracting, you can move them out of your sight by moving your eyes up and down. This technique could help move the floaters away from the visual field. If there are numerous eye floaters and they are dense, the eye doctor may consider a surgical procedure called vitrectomy. During this procedure, the vitreous body and its floating particles are removed and replaced with a solution of salt. Doing this would help to improve your vision dramatically.
If your experiencing flashes and floaters, please make an appointment with your local optometrist so they can rule out any debilitating eye problems. Early detection is key to treatment success.